Regions
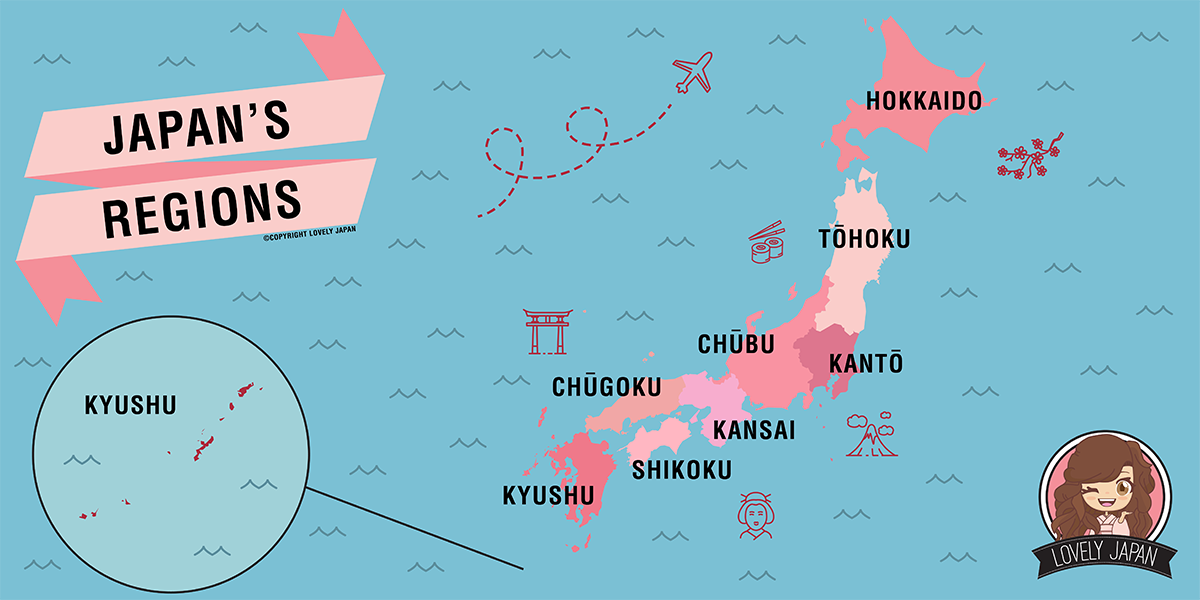
Hokkaido
Northernmost island and icy frontier. Famous for its wide open spaces and snowy winters.
Tohoku (Aomori, Iwate, Akita, Miyagi, Yamagata, Fukushima)
Largely rural north-east part of the main island Honshu, best known for seafood, skiing and hot springs.
Kanto (Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba, Tokyo, Kanagawa)
Coastal plain of Honshu, includes the cities of Tokyo and Yokohama.
Chubu (Niigata, Toyama, Ishikawa, Fukui, Yamanashi, Nagano, Shizuoka, Aichi, Gifu)
Mountainous middle region of Honshu, dominated by the Japan Alps and Japan's fourth-largest city Nagoya.
Kansai (Shiga, Mie, Kyoto, Osaka, Nara, Wakayama, Hyogo)
Western region of Honshu, ancient capital of culture and commerce, including the cities of Osaka, Kyoto, Kobe and Nara.
Chugoku (Tottori, Shimane, Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi)
South-westernmost Honshu, a rural region best known for the cities of Hiroshima and Okayama.
Shikoku (Kagawa, Ehime, Tokushima, Kochi)
Smallest of the four main islands, a destination for Buddhist pilgrims, and Japan's best white-water rafting. Largest cities Takamatsu and Matsuyama.
Kyushu (Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Oita, Kumamoto, Miyazaki, Kagoshima)
Southernmost of the four main islands, birthplace of Japanese civilization; largest cities Fukuoka and Kitakyushu.
Okinawa
Semi-tropical southern island chain reaching out toward Taiwan; formerly the independent Ryukyu Kingdom until it was annexed by Japan in 1879, its traditional customs and architecture are significantly different from the rest of Japan.